Ukraine crisis briefing
Powered by
Download GlobalData’s Ukraine Crisis Executive Briefing report
- ECONOMIC IMPACT -
Latest update: 16 September
Alongside the military strains visible on the Russian side is the prospective intensification this winter of Ukraine’s financial and energy crisis, aggravated by Russian military strikes on electricity and other civil infrastructure. However severe they may prove; such strains do not signify collapse.
Major European governments, with crucial support from the US, will use their fiscal heft to withstand the shock to the European economy from the interruption of most Russian piped gas exports and to provide the necessary unconditional support for Ukraine.
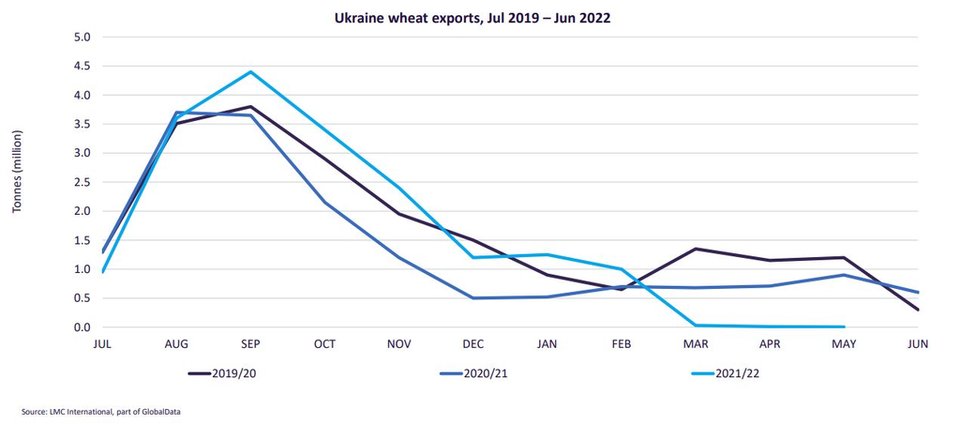
War disrupts Ukrainian energy and agriculture
Some reports suggest up to 30% of Ukrainian farmers will not plant winter crops, and the closing or the Nord 1 pipeline to Europe has led to a spike in natural gas prices, although oil prices have recorded double digit declines since the end of July.
GDP growth to stagnate and inflation rate set to rise amid war
GlobalData now forecasts that the world economy will grow at just 2.9% in 2022, following 5.9% growth in 2021. At the same time, the global inflation rate is now projected to rise to 8% in 2022 from 3.5% in the previous year, up from 7.5% in the last report.
- SECTOR IMPACT: POWER -
Latest update: 16 September
Impacts on Ukraine
Ukraine’s state-owned nuclear operator Energoatom has completely shut operations at the Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant to mitigate the fear of radiation discharge as war has intensified in the region.
Impacts on Russia
Gazprom, the Russian state-owned gas monopoly supplier has cut gas supply to Europe after announcing that a leak has been detected in the Nord 1 gas pipeline, which would take indefinite amount of time to fix.
Energy price impact
The G7 countries have agreed a plan to put a ceiling on Russian oil prices. The cap is expected to be introduced at the same time as planned EU embargoes on Russian oil kick in, 5 December for crude and 5 February for refined products, such as diesel. The level of the cap is still being discussed.
Sanctions impacts
Russia’s natural gas exports by pipeline to the European Union and the UK declined by almost 40% during the first seven months of 2022, compared with the same period in 2021 and by almost 50% compared with the previous five-year average.